Ning Yang
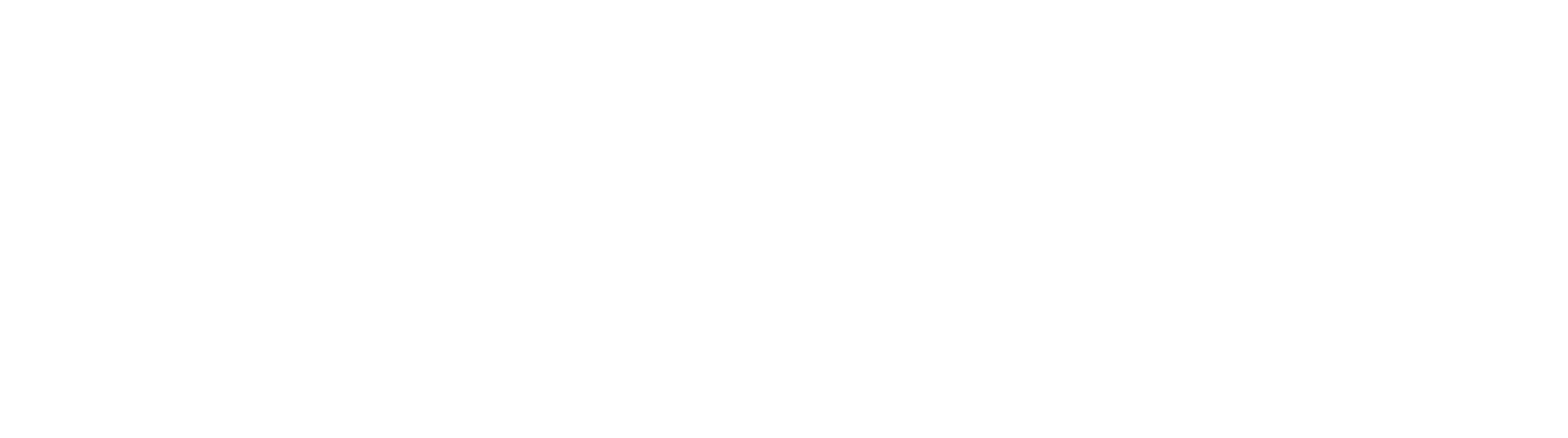
‘If they sound like a man, hang up’ – how transphobia became rife in the gender-based violence sector
gal-dem's investigation into the sector reveals an underbelly of transphobia that has alienated trans survivors and pushed some workers towards a collective fightback.
Moya Lothian McLean
01 Feb 2021
Trigger warning: transphobia, transmisogyny
It was at the tail end of 2017 when Cora*, a frontline worker for a south London organisation supporting women who have survived sexual violence, realised that undercurrents of transmisogyny had become a new precedent for her workplace.
“I just remember there being far more comments like ‘Yeah we only support real women’,” Cora says.
Both visibility and hostility were on the rise for trans people in the UK thanks to proposed reform to the Gender Recognition Act. As a result, many junior workers were attempting to ensure inclusivity for trans survivors. But senior staff, made up of cis women, responded by shutting down the conversation altogether.
Cora’s organisation is not an island. On record, gal-dem has spoken to workers in the violence against women and girls [VAWG] sector, who have spent time at organisations including Imkaan, Rape Crisis, Refuge, Amnesty International and Liberty, academics working in the field of gender studies and members of the dedicated gender-based violence branch of union United Voices of the World. Of the workers who spoke to gal-dem, all were too terrified of reprisals to use their real names.
Alongside interviews, gal-dem examined records of public statements made by senior members of organisations like Nia, Southall Black Sisters, and the Centre for Women’s Justice. What emerges is a hostile landscape to navigate for trans survivors of sexual violence, both in accessing immediate frontline services and overcoming ideology that seeks to shut them out of the gender-based violence sector (GBV) in general. With one in six trans women experiencing domestic violence between 2017 to 2018 (and more recent figures suggesting violence against trans people remains high), this landscape’s hostility is undoubtedly already having damaging effects.
At Cora’s organisation, it quickly became apparent that senior staff were deliberately shelving pressing trans-related issues, in the hope that they would disappear altogether. Cora alleges that the CEO Rachel*, who had served as the head of the organisation for nearly three decades, encouraged a culture that was openly hostile to trans women.
Regular requests for the centre’s policy regarding trans women were lodged, but the policy didn’t exist. A lone attempt to create a gender inclusion policy ended with the firing of the employee tasked with producing it. As Cora remembers it, the day after the employee submitted their work, they were told their position was no longer viable. Although it wasn’t cited as a factor in the decision, Cora believes the incident speaks for itself. The policy was not adopted by the centre.
Staff soon began to organise and demand an outright commitment to supporting trans people, pushing the transphobic views of senior management into the open.
“We do get abusive callers on the helpline. But they present as men, not as trans women”
Cora remembers one member of the counselling department declaring that it was “unsafe” for cis survivors using the centre’s services to have people in the building who had not fully medically transitioned. She was challenged by Cora and her colleagues, who explained that this transmisogyny went against the fundamental principles of sexual violence workers: that you must believe survivors.
“I find it fascinating in a horrific way that this bedrock of [sexual violence services] is thrown out of the window immediately,” Cora observes. “They say, ‘Oh, men will just call up pretending to be women, and saying that they’re trans to get into the space to enact harm’.
“Do you not think we are trained in such a way that we are able to speak to someone and know? Because we do get abusive callers on the helpline. But they present as men, [not as trans women]… When you get a call like that, you know. As soon as you pick up the phone, it doesn’t feel right. The gut that you’ve honed so wonderfully and beautifully to do this work, it knows”.
When Cora and her colleague refuted transmisogynistic claims, the goalposts shifted. Senior staff instead claimed they weren’t equipped to work with trans women because they wouldn’t “understand” their experience with sexual violence. Tellingly, one staff member who used such a defence said they would feel comfortable supporting trans men who had “experienced violence as women” – revealing that they didn’t recognise trans men as men.
“There is a real focus on the penis,” Cora says.
Cora left the organisation a few years ago, in part due to the virulent transmisogyny that had become the norm. Rachel stepped down from the CEO position in 2020, after what Cora describes as “successful unionising efforts” from the organisation’s staff. While the new CEO is “far more inclusive”, Cora says, her former co-workers report that hostility to trans survivors persists.
“The problem is much deeper than top down,” she says. “It runs through most of the services.”
Women vs women
Cora’s organisation has become part of a larger war. Transphobia – or ‘gender criticism’ as its proponents like to position it – has become a battleground for a small but powerful pocket of UK feminists. With access to mainstream media platforms, large social media audiences and political influence, these ‘gender-critical’ feminists are attempting to turn trans people from a minority group into a full-scale moral panic.
But where does the antagonism towards trans people in the VAWG sector come from? Academic Alison Phipps, professor of gender studies at the University of Sussex, links it to “political whiteness”. Transmisogyny in the UK is focused on violence against white, cis women and “lasers in” on the male body as the source of that violence, Phipps explains. “There’s a lot of straight, [white], privileged [cis] women involved. Whiteness has a lot to do with it. Whiteness and class privilege.”
Weaponising woundedness against marginalised groups has always been a core component of white womanhood and political whiteness, adds Phipps. “It’s Carolyn Bryant [Emmett Till’s accuser] all over again,” she says. “[Trans-exclusionary feminism] is grounded in fear and, in some cases, a hatred of the Other and a deep need for protection.”
For the last few years, the central objective of trans-exclusionary feminists – achieved for the time being – was to prevent reforms to the Gender Recognition Act that promised to make the process of legally identifying as trans or non-binary (which isn’t a recognised legal identity at the time of writing) far quicker.
A spotlight fell on women-only services for survivors of sexual and domestic abuse as a result. In order to provide rationale for their aversion to trans individuals, the gender-critical cabal alighted upon whipping up fear around trans women who might need to access such spaces. For trans-exclusionary feminists, the argument goes that allowing self-determination through GRA reforms would open up ‘single-sex’ sites to ‘predatory men’, who would supposedly pretend to be women in order to perpetuate abuse.
Yet trans women, with some exceptions, already have access to single-sex spaces under the 2010 Equality Act, which would remain unchanged by any amendments to the GRA. Furthermore, no countries that already allow self-determination have reported any sudden trend of cis men engaging in such behaviours. A 2018 Guardian investigation found that Ireland, which introduced self-determination in 2015, has seen “no evidence” of new legislation leading to men “falsely declaring themselves female”.
No matter; gender critical feminists in the UK still insist that the sex assigned at birth must decide who is admitted to women-only spaces. Never mind that multiple global studies show that trans women report sexual and domestic violence at double the rate of cis women (with trans women of colour facing the most peril) – but, as with cis women, the perpetrators were most likely to be men.
“Trans-exclusionary feminism is grounded in fear and, in some cases, a hatred of the Other”
Phipps believes many transphobic, white radical feminists also think that acknowledging their own privileges compared to the likes of trans women is tantamount to erasing their traumatic experiences. “It’s as if they think ‘if you tell us we’re privileged because we’re cis, that means we haven’t been raped or haven’t experienced these awful things’,” she observes. “Well of course you have and that’s awful and it’s because of your gender. But that doesn’t mean you don’t also have race and class and cis privileges.”
In the VAWG sector in particular, Phipps says there is the feeling of “living in the past”, with particular aping of the 1970s women’s liberation movement. It’s a notable reference point for trans-exclusionary feminists, many of whom experienced the movement as young women. But they’ve created a warped pastiche that erases contemporary critiques of white radical feminism that were made at the time, says Phipps.
Radical feminist texts of the 1970s were often trans-inclusive. While the likes of Andrea Dworkin held problematic notions around issues like sex work, they weren’t trans-exclusionary and didn’t see the body in “essentialist” terms. In stark contrast, trans-exclusionary feminists of the present, do.
The crusade against trans women is tragic, says Phipps, a focus of energies on completely the wrong target. “There is a war against women worldwide,” she says. “But trans women are also [victims] of this war, not the perpetrators.”
A worsening situation
Frontline VAWG workers say that hierarchical power structures mean transmisogyny is often sanctioned from the top. Close ties between powerful names in the sector mean it is hard to challenge for fear of being blacklisted from multiple organisations. Nevertheless, those who spoke to gal-dem said they did so out of a desire to lift a lid on the situation and encourage more scrutiny of the reality behind the press releases.
“I couldn’t [continue to] work for an LGBTQ charity that poses like it’s inclusive,” says Lily* a former employee of one high profile organisation serving sufferers of domestic violence. She says she witnessed virulent transmisogyny during her time there.
One incident occurred when Lily’s workplace was developing a helpline for clients. She and her colleagues were concerned that the helpline wasn’t inclusive enough because the organisation didn’t have a gender inclusion policy. They asked for clarity on who the helpline was for.
“The reply from [Martha* the director of operations at the organisation] and another senior staff member was that ‘if they sound like a woman on the phone, talk to them’,” remembers Lily. “‘If they don’t sound like a woman, it doesn’t matter if they say they are, hang up. We’re not supporting them’.”
Lily also heard references to “men-women”, assertions that only “biological women” should have access to refuges and accusations from a senior staff member that junior employees were behaving like “perpetrators” by supporting trans-inclusivity as it put them on the side of “men”.
“They told us: if they don’t sound like a woman, it doesn’t matter if they say they are, hang up”
According to those present at one group meeting, a staff member declared that there needed to be a “step back” on giving “privileges” to trans women because they were damaging support being provided to “women”. The staff member is also alleged to have said this view was the organisation’s “policy” as well, blaming trans-inclusive terms like “person with a cervix” for having “erased” cis women.
Allegations of increased transmisogyny are mirrored across the sector. Eva, a non-frontline VAWG worker who has spent time at multiple women’s organisations, says she became aware the issue wasn’t going away in 2016.
One early indicator came when Eva posted on a social media platform, from the official account of one prominent organisation about the death of a trans woman in a men’s prison. The next day, she says, she was handed a social media policy that “explicitly stated” she was not allowed to post about trans people anymore.
Even in supposedly inclusive environments within the women’s sector, transmisogyny simmers, says Eva. Her organisation, which focuses on ending gender violence for Black women and girls, still throws up obstacles when it comes to officially including trans women, including a failure to create and implement a trans-inclusive policy.
She also believes economic factors have caused trans women to become a lightning rod of the frustrations and fears of some cis women within the field.
As she explains it, many of the more senior positions in the modern VAWG sector are filled by women who have been there since its foundation. They’ve seen funding and resources chipped away by successive governments, resulting in resignation that “they’re never going to win a victory over the government”.
Collective fightback
Eva stresses that she doesn’t believe the sector itself to be transphobic and that younger, more junior members of staff tend to be fiercely trans-inclusive. There are some power players in the sector attempting to make change.
Cara English, head of public engagement at trans-led charity Gendered Intelligence (GI), says that she’s been approached by CEOs of VAWG organisations to provide training on trans inclusivity to staff. But plans have been stymied by the individualised structures of centres and refuges subject to the decisions of CEOs.
“[GI] met with the CEO of probably the largest VAWG service provider in the UK,” Cara recounts. “She was saying transphobia is very prevalent and she’s not content with it. But there’s not really a great deal they can do apart from bringing training from trans organisations in house.”
The situation is particularly dire in England and Wales. Scotland however, while no utopia for trans survivors, offers a look at how trans inclusivity can begin to be implemented.
Simple commitments have made huge differences to services says Mridul Wadhwa, manager of the Forth Valley Rape Crisis Centre in central Scotland. One such initiative is the LGBT Charter, a programme which includes education on trans inclusion. Completion of the course sees organisations given a digital “badge” to display on-site, letting survivors know they are an inclusive space.
As a trans woman managing a refuge, Wadhwa says she has received “unnecessary negative attention”, despite over 15 years of experience in the sector. After a recent bid to become an SNP candidate, she was even hit with accusations online that she had “lied” by not disclosing her trans identity when she was first employed in 2005 by Shakti Women’s Aid.
“This was before the Equality Act,” she remembers. “I said in an interview that if [Shakti Women’s Aid] had known I was trans, they would not have hired me. But everyone knew I was trans when I was [hired] for my current position.”
Wadhwa’s experience has taught her that many trans women survivors seeking support are too fearful of being faced with transmisogyny to approach services in the first place. This renders them invisible within the sector, despite being a group disproportionately affected by sexual and domestic violence.
“You have to be explicit that you’re inclusive, you cannot assume that people know,” Wadhwa says, adding that as a member of intersecting minority groups, she expects to be “oppressed in every place I go”.
“You have to wear the badge – these things make a huge difference, as well as word of mouth recommendations spread by survivors who have worked with you. There also needs to be a trans-inclusive workplace policy”.
“You have to be explicit that you’re inclusive, you cannot assume that people know”
For workers who want to push back against institutionalised transphobia, organising collectively offers a glimmer of hope.
Cora tells me that challenging transphobia was a key driver of unionising efforts by herself and colleagues who didn’t feel “safe” enough to do so as individual unprotected workers. Meanwhile, a spokesperson for the workers union United Voices of World, which has a dedicated arm for workers in the gender-based violence sector, says that one of the union’s goals is fighting transphobia in the field.
Those pushing for change recognise that while the pocket of women they’re up against is small and unrepresentative, they’re powerful, with a reach that extends into the upper echelons of journalism, the legal system and the halls of Westminster. All workers who spoke about the transphobia they’d witnessed feared the impact their whistleblowing might have on the sector, which they stressed still does vital work. But as Eva puts it, if the services are not working for all women, they’re ultimately failing in their purpose.
“If frontline services aren’t working for all women, they’re not working for any of us really,” she says. “They’re not rooted in our liberation or justice.”
Pulling trans-inclusive training in-house, as suggested by Cara English is also a key goal. But it will take determination and demand on the part of the workers within those organisations.
And ultimately, it will need the battle-weathered radical feminists perpetuating transmisogyny in the the GBV sector to do something they are unused to: rethink the dogmatic approach that has for so long served as a survival technique but now works to oppress a deeply vulnerable group of women.
The entire situation is, says Cara English, a “degradation”.
“The fact we’re still in a position when we’re actively having to humanise trans women and trans people to services that would seek to exclude us, in order to get into places that we should have the right to access… this is just an obscene position to be in,” she adds.
“It’s a wholesale failure to take into account the needs of trans people. It’s embarrassing. The issue isn’t that trans women aren’t accessing VAWG services. It’s that people aren’t seeing this joint fight against the patriarchy and the oppression of all women.
“That’s where we need to be focusing our attention. It’s about solidarity between all people who need help and an escape”.
*Names have been changed to protect identities
In the UK, call Galop’s National Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual and Trans+ Domestic Abuse Helpline on 0800 999 5428, the national domestic abuse helpline on 0808 2000 247 or visit Women’s Aid. In the US, the domestic violence hotline is 1-800-799-SAFE (7233). Other international helplines can be found via www.befrienders.org

The architect inspiring Muslim girls everywhere

My partner broke the boundaries of our open relationship
How Pakistan’s Khwaja Sira and transgender communities are fearing and fighting for their futures